介绍图数据库中属性图的查询语言——Cypher,这是一篇CCF A类文章,发表于数据库顶会SIGMOD,讲得很详细很不错!原文链接
@Authors:Nadime Francis,Alastair Green,Paolo Guagliardo
@Published in: SIGMOD Conference 2018: 1433-1445
@Presented by: Yina Lv , Time: Qct 10, 2018
@Action:October 11, 2018 9:21 AM
Schema
- 介绍了属性图和Cypher语言的语法结构
- 以事例的形式讲述Cypher查询过程
- Cypher中的核心元素:数据模型和查询语言
- pattern matching
- 比较Cypher语言和其他数据库查询语言的特征,描述其扩展性、先进性,并将发展成Cypher10
1.Introduce
1.1 Property graph database
Property graph databasesuch as Neo4j,JanusGraph and Sparksee have become more widespread in industry and academia.- used in multiple domains, such as master data and knowledge management, recommendation engines,fraud detection, IT operations and network management, authorization and access control , bioinformatics , social networks, software system analysis , and in investigative journalism.
- Benefits:
- explicit support for modeling graph data
- native indexing
- storage for fast graph traversal operations
- built-in support for graph algorithms
- the provision of graph language
1.2 Cypher
-
Cypher: a well-established language for querying and updating property graph databases- began life in the Neo4j product, but has now been implemented commercially in other products such as SAP HANA Graph, Redis Graph, Agens Graph (over PostgreSQL) and Memgraph.
- Cypher is also used in several research projects (e.g., Ingraph ,Gradoop , and Cytosm) as well as in recent or incubating open-source projects, such as Cypher for Apache Spark and Cypher over Gremlin.
- Cypher是线性查询,输入property graph,输出table
- 数据更新:
CREATE: creating new nodes and relationshipsDELETE: moving entitiesSET: updating propertiesMERGE: try to match the given patten,and creates the pattern if no match was found
2.Example
Graph Schema:
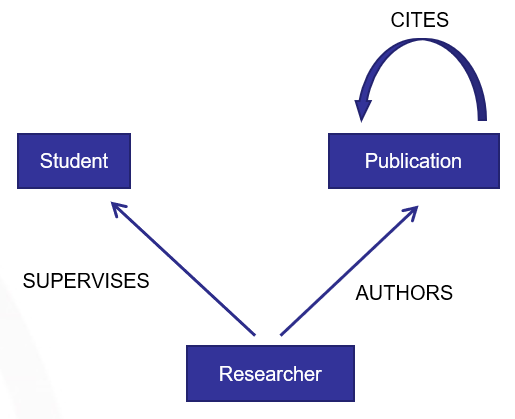
- PS:图中有三个label,分别是
researcher、Student、Publication,三种关系:SUPERVISES、AUTHORS、CITES - 研究员有指导的学生,研究员发表刊物,那么就是某刊物的作者,刊物之间可以互相引用。
- CITES我画成了自循环,但是大家这样理解比较合适:一个刊物可以被另外一个刊物引用。
Big graph:(整个数据库的属性图如下)
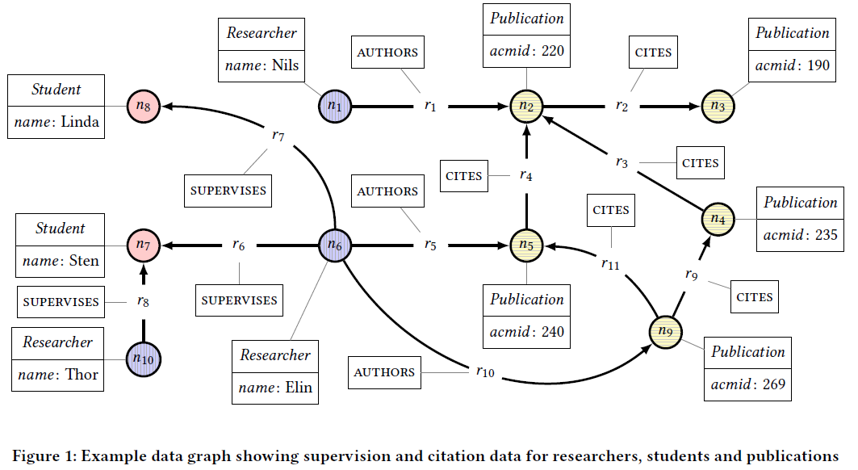
2.1 查询示例语句如下:

Q: 返回图G中每个researcher的name,他们所supervises指向的学生数,以及他们撰写的出版物被其他出版物直接或间接引用的次数。
我们分析每一个语句的查询结果。
MATCH (r:researcher)
- 在这句语句中,r是instance,researcher是label
OPTIONAL MATCH (r)-[:SUPERVISES]->(s:Student)
OPTIONAL MATCH与MATCH的区别在于,OPTIONAL MATCH会返回查询结果为NULL的记录。SUPERVISES为关系的label,(r)-[:SUPERVISES]->(s:Student)表示找出researcher对应指导的学生实例- 1、2两句语句执行结果如下:
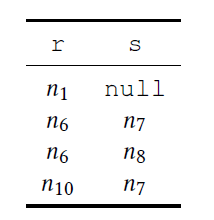
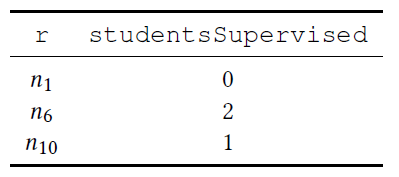
WITH r,count(s) AS studentsSupervised
- AS:取别名
- count(s):计算上面找出的学生数
- 在with语句前面部分找出的子图作为with语句后面查询的驱动表
MATCH (r)-[:AUTHORS]->(p1:Publication)
- n10不写是因为
MATCH不返回NULL的记录

OPTIONAL MATCH (p1)-[:CITES*]->(p2:Publication)
CITES后面的*表示任意步长,当然也可以指定步长,比如CITES*1..3表示跳一步到三步- 结果中的n9有两个是因为n9可以有两条路径达到n2
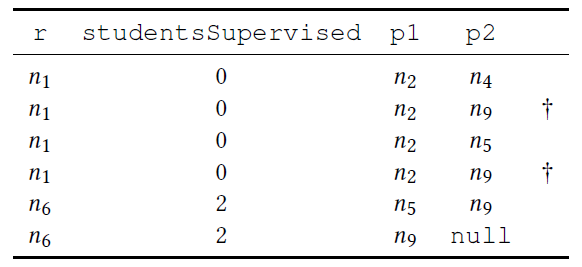
6、7. RETURN r.name,studentsSupervised,count(DISTINCT p2) AS citedCount
- 返回最后的结果

2.2 Examples from industry
Q1: A real-world query from the network management domain

- The query returns the component that is depended upon – both directly and indirectly – by the largest number of entities.
order by: 排序,可指定增序还是降序LIMIT:取几行记录- MATCH中的箭头可以向左也可以向右
Q2: A query in the domain of fraud detection
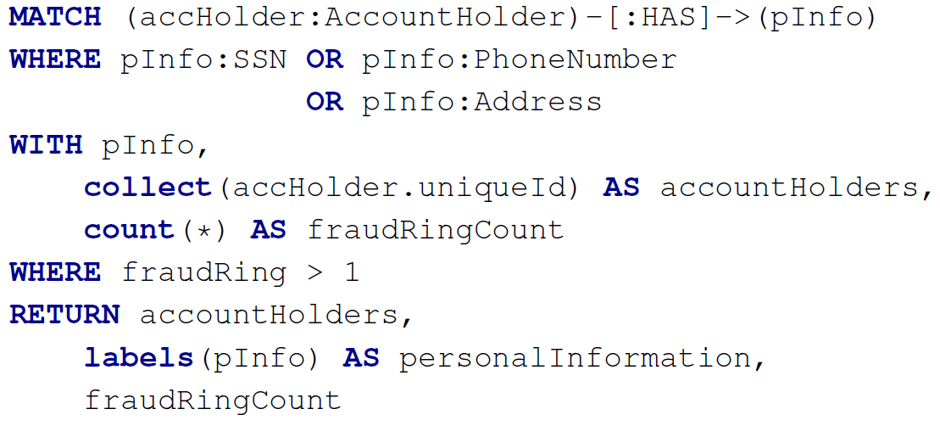
- pInfo后面三个为label,可以将pInfo理解为节点信息,那么语句的意思就是信息可以是SSN,或者PhoneNumber,或者Address
- WHERE后面跟着的是一些过滤条件,这些过滤条件也可以放在MATCH后面,比如第一个where后面跟着实例的标签,那么也可以写成
MATCH (accHolder:AccountHolder)-[:HAS]->(pInfo:SSN:PhoneNumber:Address) collect(): 返回表达式表示的值,放入list并返回labels(): 返回一个节点的所有标签,以list的形式返回count(*): 用于计算匹配的行数
3.FORMAL SPECIFICATION
-
The key elements of Cypher are as follows:
data model, that includes values, graphs, and tables;query language, that includes expressions, patterns, clauses, and queries.
-
Property graphs
- We now refer to the property graph in Figure 1 and show how, for a sample of its nodes and relationships, it is formally represented in this model as a graph
G = (N, R, src, tgt, ι, λ, τ ). - N: 实例
- R: 关系
- src:从关系到源节点这样的存储结构
- tgt:从关系到目标节点这样的存储结构
- ι(n1,name)=Nils: 节点1的名字叫Nils,存储(key,value)的形式
- λ(n1)={Student}: 存储节点label
- τ®=AUTHORS: 存储关系的label
- We now refer to the property graph in Figure 1 and show how, for a sample of its nodes and relationships, it is formally represented in this model as a graph
good luck!
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏 微信打赏
微信打赏